9.3.5 Coordinate Covalent Bond
This is the fifth lecture from Chapter 3: “Chemical Bonding” in the new Class 9 Chemistry book (Punjab Board – PCTB). It discusses the formation of metallic bonds in metals. The lecture also includes a multiple-choice quiz, short question and long question notes.
MCQs Based Quiz
Short Questions
Q1. Write some characteristics of metals.
- Metals usually show metallic luster.
- They have high melting and boiling points.
- They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- They are usually hard and heavy.
- They can be shaped into wires or sheets when pressure is applied.
Q2. Why is it relatively easy to remove electrons from metallic atoms?
Metals have low values of ionization energy. Which means their nuclei do not hold the outermost electrons tightly, making it easier to remove them.
Q3. Why is it relatively easy to convert a metallic atom into a cation?
Because of their low ionization energy, metal atoms do not strongly hold their outer electrons. This makes it easier to remove electrons and form positively charged ions (cations).
Q4. What do you mean by the “sea of electrons” in metals?
In metals, the outermost electrons leave their atoms and move freely in the empty spaces between the metal atoms. These free electrons are not attached to any specific nucleus, forming a “sea of electrons.”
Q5. What are mobile electrons in metals?
Mobile electrons are the outermost electrons in metal atoms that move freely in the spaces between atoms. Since they are not bound to any specific nucleus and can move throughout the metal.
Q6. What is a metallic bond?
A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond in which positively charged metal ions are held together by a sea of mobile electrons.
Q7. On what factors does the strength of a metallic bond depend?
The strength of a metallic bond depends on:
- The positive charge on metallic ion
- Number of mobile electrons released by each metal atom
Q8. Why is the metallic bond in magnesium metal stronger than that in sodium metal?
The strength of a metallic bond depends on the charge of the metallic cation and the number of electrons released by the metal atoms. Magnesium metal releases two electrons and forms a +2 cation, whereas sodium releases only one electron and forms a +1 cation. Therefore, magnesium has stronger metallic bonding than sodium.
Q9. Why is the metallic bond in magnesium stronger than that in sodium?
Magnesium atoms release two electrons and form +2 cations, while sodium atoms release only one electron to form +1 cations. More electrons and a higher positive charge make the metallic bond in magnesium stronger than in sodium.
Q10. Why is the melting point of magnesium higher than that of sodium?
Since magnesium forms stronger metallic bonds due to its +2 charge and release of two electrons, it requires more energy to break these bonds. This results in a higher melting point compared to sodium.
Q11. What makes metals good conductors of heat and electricity?
The presence of free moving (mobile) electrons allows metals to conduct heat and electricity
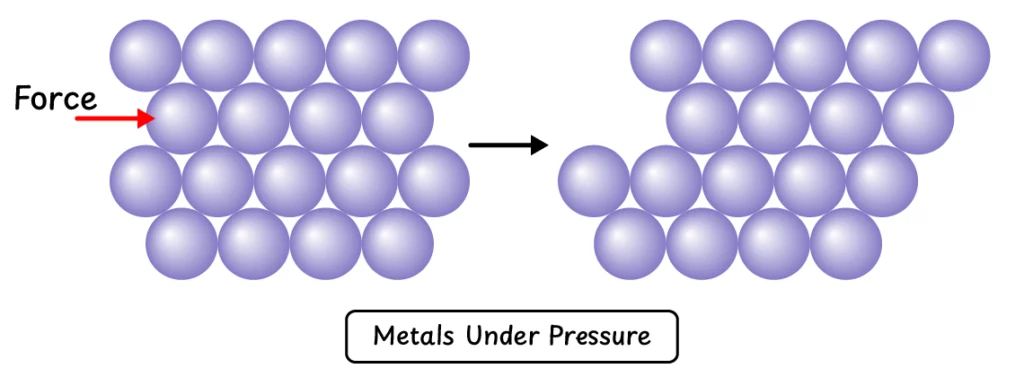
Q12. Why are metals hard and heavy?
Metals are hard and dense because their atoms are packed in tightly held layers. These closely stacked layers make metals strong and give them weight. Under pressure, these layers slip past each other without breaking.
Q13. Why are metals bendable (malleable and ductile)?
Metals consist of layers of atoms that can slide over one another when pressure is applied. This allows metals to be drawn into wires (ductility) or hammered into sheets (malleability).
Q14. What type of atoms form metallic bonds?
Only metal atoms form metallic bonds. They have low ionization energies and easily lose their outermost electrons to create a sea of free electrons.
Q15. Give a comparison of a metallic bond with an ionic bond.
Both metallic and ionic bonds involve the loss of one or more electrons. In an ionic bond, these electrons are accepted by non-metals, forming a bond between cations and anions. However, in metallic bonding, the electrons become mobile and move freely throughout the metal.
Q16. What are some uses of metals?
Metals are used in various fields such as industries, machinery, automobiles, railways, aircraft, rockets, construction, electronics, jewelry, and electric wiring.
Descriptive Question
Q1. Write an explanatory note on metallic bond. Also discuss the factors affecting the strength of metallic bonds.
A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond in which positively charged metal ions are held together by a sea of mobile electrons.
Formation of a Metallic Bond:
- Metals have low values of ionization energy, which means their nuclei do not hold their outermost electrons firmly.
- As a result, metals can easily lose these electrons, forming metal cations.
- The outermost electrons that are freed become mobile electrons, as they can move freely in the empty spaces between metal cations.
- These free electrons are attracted to all metal cation nuclei.
- This collective attraction binds the metal cations together, resulting in the formation of a metallic bond.
- It appears as if the metal cations are submerged in a sea of free electrons.
Factors Affecting the Strength of Metallic Bond:
- The positive charge on the metal ion (the more the charge, the stronger the bond).
- The number of mobile electrons released by each metal atom
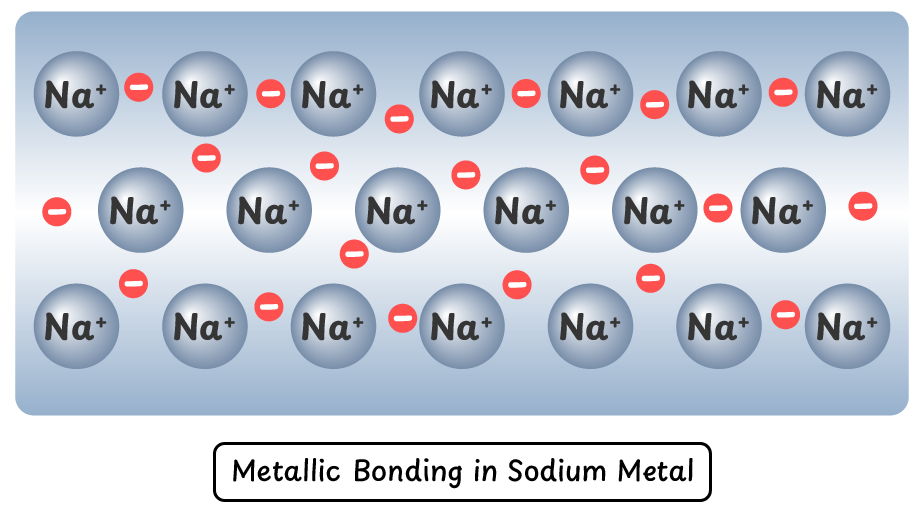
Metallic Bonding in Sodium (Na):
- Sodium atoms release only one electron, forming Na⁺ ions, resulting in weaker metallic bonding.
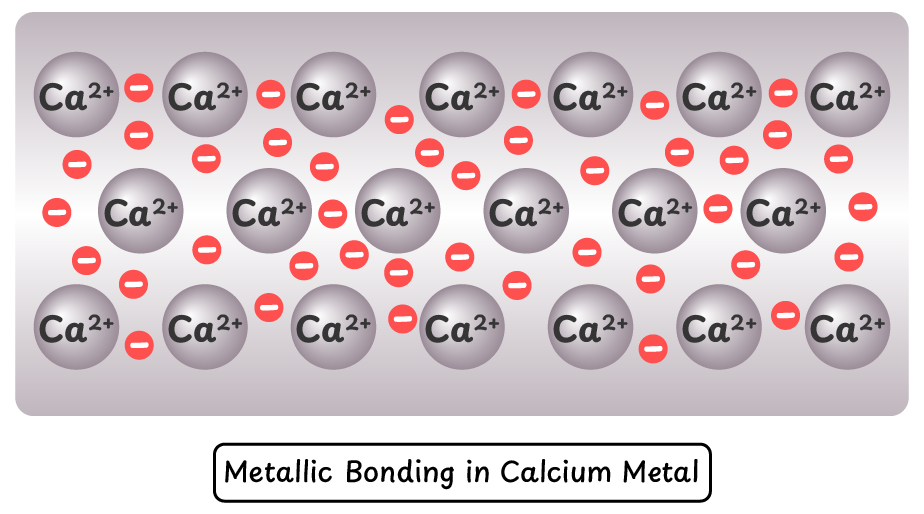
Metallic Bonding in Calcium (Ca):
- Magnesium atoms release two electrons, forming Mg²⁺ ions, resulting in stronger metallic bonding. This also explains why magnesium has a higher melting point than sodium.
Q2. Give a detailed comparison between a metallic bond and an ionic bond.
Metallic Bond
Ionic Bond
A metallic bond is formed only between metallic atoms.
An ionic bond is formed between a metal and a non-metal.
Only metallic cations are formed.
Both cations and anions are formed.
Electrostatic attractions are developed between metal cations and mobile electrons.
Electrostatic attractions are developed between metal cations and nonmetal anions.
Only electron loss occurs.
A complete transfer of electrons happens.
It contains mobile electrons.
It does not contain mobile electrons.
Substances with metallic bonds are good conductors of heat and electricity.
Substances with ionic bonds do not conduct heat or electricity in solid form.
Examples: Metallic bonds are found in elements like gold, silver, iron, copper, and sodium.
Examples: Bonds in compounds like NaCl, KCl and MgCl2
Q3. What are some properties of metals? Also explain the conductance and hardness of metals.
Properties of Metals:
- Metals usually show metallic luster.
- They have high melting and boiling points.
- They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- They are usually hard and heavy.
- They can be made into different shapes by applying pressure.
Good Conductance of Metals:
Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity because they have free and mobile electrons in them. These mobile electrons carry heat and electricity from one end of the metal to the other.
Strength and Hardness of Metals:
Due to strongly bonding between layers of metal atoms stacked on top of each other, metals are very hard and heavy. When pressure is applied, the upper layers of atoms can slip past the lower layer without breaking. As a result, metals change shape without shattering. This is why metals can be easily drawn into wires (ductility) and hammered into sheets (malleability).