9.2.7 Isotopes and their Masses
This is the seventh lecture from Chapter 2: ‘Atomic Structure’ of the new book for Class 9 Chemistry (Punjab Board – PCTB). It discuses isotopes, radioactive isotopes and their applications. The lecture includes a multiple-choice quiz, short-answer questions, and detailed long-answer notes.
MCQs Based Quiz
Short Questions
Q1. Define isotopes of an element.
Atoms of the same element having different number of neutrons in their nuclei are called isotopes of that element.
OR
Atoms of the same element that have same atomic number but different mass numbers are called isotopes of that element.
Example: Hydrogen has three isotopes, Protium ${^{1}_{1}H}$, Deuterium ${^{2}_{1}H}$ and Tritium ${^{3}_{1}H}$
Q2. Why do isotopes of an element have the same atomic number?
This is because all the isotopes of an element have the same number of protons in their nuclei.
Q3. Name the three isotopes of hydrogen and their neutron counts.
Protium ${^{1}_{1}H}$, Deuterium ${^{2}_{1}H}$ and Tritium ${^{3}_{1}H}$.
Protium does not have any neutrons, deuterium has one neutron and tritium has two neutrons.
Q4. List all the isotopes of carbon element.
${^{12}_{6}C}$, ${^{13}_{6}C}$ and ${^{14}_{6}C}$
Q5. Is there an atom that has only two sub-atomic particles?
Yes there is only one such atom, protium (${^{1}_{1}H}$). A protium atom has only 1 proton and 1 electron.
Q6. What do you call atoms like C-12, C-13 and C-14? What is the difference between these atoms?
C-12, C-13 and C-14 are called isotopes of carbon. All of them have different number of neutrons in their nuclei and different physical properties.
Q7. Why do isotopes exhibit similar chemical properties?
This is because chemical properties depend on the number of electrons in an atom, and all the isotopes of an element have the same number of electrons due to the same atomic number.
Q8. Give an example of atoms that have similar chemical properties but different physical properties.
Protium ${^{1}_{1}H}$, Deuterium ${^{2}_{1}H}$ and Tritium ${^{3}_{1}H}$ are example of such atoms. They have similar chemical properties but different physical properties. they are called isotope of hydrogen.
Q9. Is it true that all the atoms of an element are identical to each other?
No, this is not true. An element can exist in different forms called isotopes. These isotopes have different numbers of neutrons and different physical properties.
Q10. Why do isotopes of an element show same chemical properties while their physical properties are different?
Chemical properties of an atom depend on its number of electrons. But some of the physical properties depend on the mass of that atom. Therefore, because all the isotopes have same number of electrons in them, their chemical properties are same, but due to different mass numbers their physical properties are different.
Q11. Why do all isotopes of an element occupy same spot on the periodic table?
This is because elements in the periodic table are arranged in ascending order of atomic number, and all isotopes of an element have the same atomic number.
Q12. How would you define a radioactive isotope?
A radioactive isotope is an isotope of an element that has an unstable nucleus and emits radiation.
Example: Hydrogen-3 (Tritium), carbon-14 and technitium-99
Q13. Define radioactivity.
Radioactivity is the process by which a radioactive isotope emits excess energy in the form of radiation.
Q14. What is radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is the process in which a radioactive isotope emits radiation and transforms into another element.
Example:
$\ce{^{238}_{92}U -> ^{234}_{90}Th + \text{energy}}$
Q15. How does bismuth-210 undergo radioactive decay?
Bismuth-210 decays into thallium-206 as followed:
$\ce{^{210}_{83}Bi -> ^{206}_{81}Tl + \text{energy}}$
Q17. Through what steps does uranium-238 decays into Pa-231?
Step 1:
$\ce{^{238}_{92}U -> ^{234}_{90}Th + \text{energy}}$
Step 2:
$\ce{^{234}_{90}Th -> ^{231}_{91}Pa + \text{energy}}$
(In the book, it says that Th-234 decays into Pa-231, but this is incorrect. Th-234 actually decays into Pa-234.)
Q18. How are radioactive isotopes used in medical imaging?
A small amount of radioactive fluid, such as technetium-99m, is injected into the patient. Then a special camera is used to monitor the movement of that radioactive fluid into the body, which helps in diagnosing diseases.
Q19. Give one use of technitium-99m.
Tecnitium-99m is used in medical imaging for organs like brain and lungs. Doctors use a special camera to monitor the movement of this radioactive fluid inside the patient’s body.
Q20. Why does a radioactive isotope emit radiation?
A radioactive isotope emits radiation because its nucleus is unstable and has excess energy. By emitting radiation, it releases this energy and becomes more stable.
Q21. Give an example of radioactive isotope which disintegrates into a stable atom.
Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope which decays into nitrogen-14, which is a stable atom.
$\ce{^{14}_{6}C -> ^{14}_{7}N + \text{energy}}$
Q22. What is the principle behind carbon dating?
In carbon dating, scientists measure the proportion of carbon-14 (C-14) remaining in an old organic sample (like wood or bone). Older samples contain less C-14, which helps estimate their age.
Q23. Applications of radioactive isotopes in medical field?
- Used in medical imaging to scan organs like the brain and lungs.
- Used to diagnose and treat diseases like cancer and thyroid disorders.
Q24. How can a radioactive isotope ionize an atom?
Radiation from a radioactive isotope (such as radium-226) collides with an atom, knocking electrons away from it. This process converts a neutral atom into a cation.
$\ce{Na ->[\text{Energy}] Na+ + e-}$
Descriptive Question
Q1. What are isotopes? How can atoms of the same element have different properties?
Atoms of the same element that have same atomic number, but different mass numbers are called isotopes of that element.
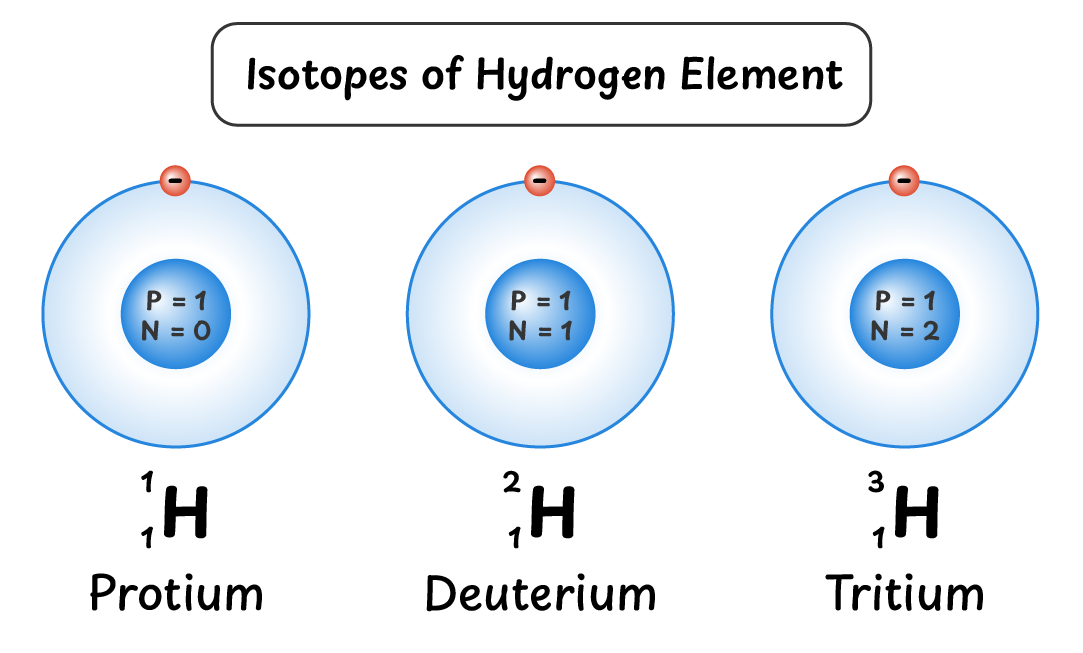
Isotopes of Hydrogen:
Hydrogen element has three isotopes:
- Protium ${^{1}_{1}H}$: 1 proton and 1 electron
- Deuterium ${^{2}_{1}H}$: 1 neutron, 1 proton and 1 electron
- Tritium ${^{3}_{1}H}$: 2 neutrons, 1 proton and 1 electron
Isotopes of Carbon:
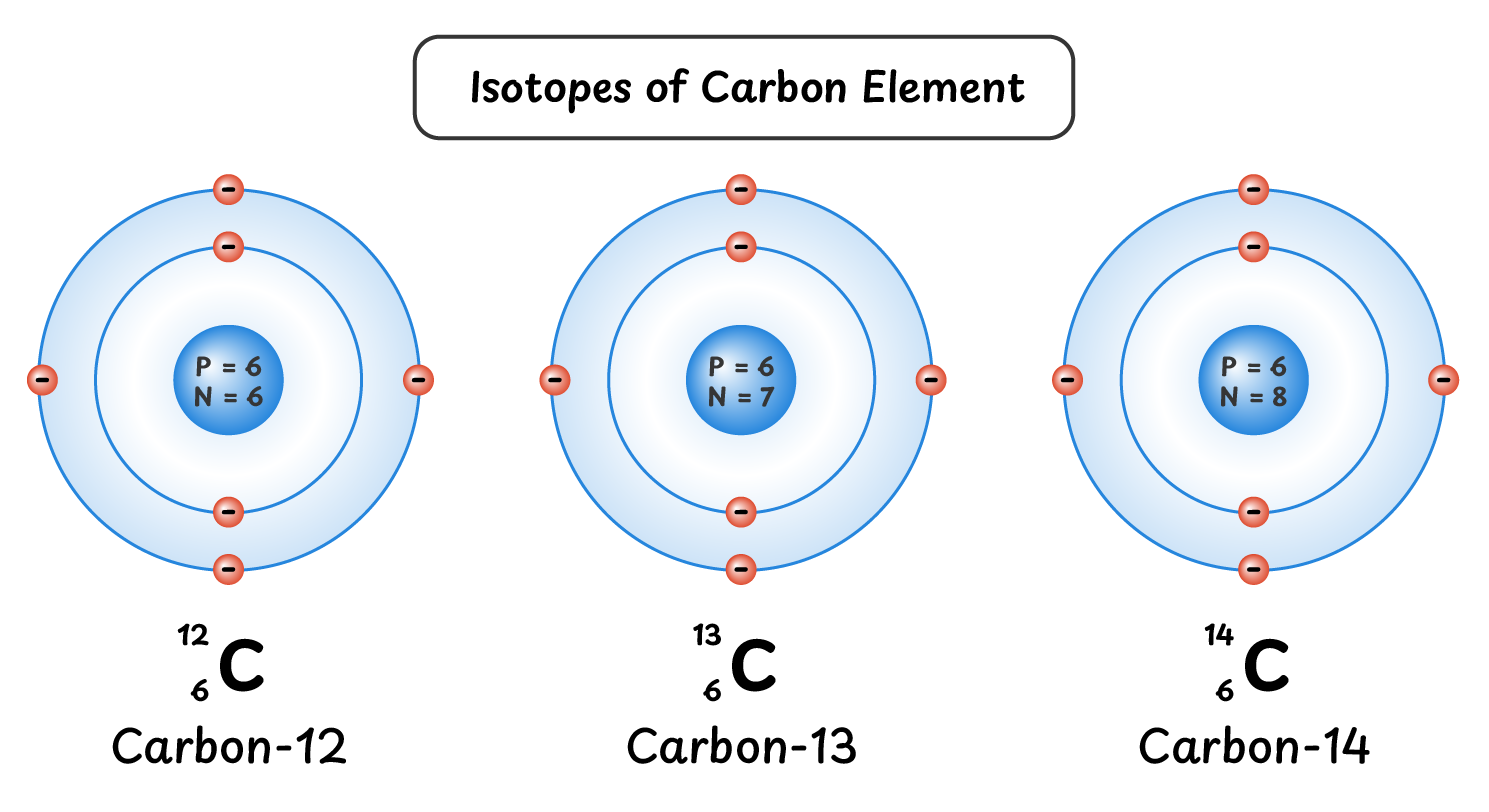
Carbon also has three isotopes:
- Carbon-12 ${^{12}_{6}C}$: 6 neutrons, 6 protons and 6 electrons
- Carbon-13 ${^{13}_{6}C}$: 7 neutrons, 6 protons and 6 electrons
- Carbon-14 ${^{14}_{6}C}$: 8 neutrons, 6 protons and 6 electrons
Properties of Isotopes:
- Isotopes have same atomic number, which means they have same number of protons and electrons.
- Because chemical properties depend on number of electrons, all the isotope of an element has same chemical properties.
- However, due to different mass numbers, their physical properties are different.
Q2. Write a note on radioactive isotopes. How are elements transformed into other elements?
A radioactive isotope is an isotope of an element that has an unstable nucleus and emits radiation.
Radioactivity is the process by which a radioactive isotope emits excess energy in the form of radiation. Radioactivity is a physical property.
Example: Hydrogen-3 (Tritium), carbon-14 and technitium-99
Radioactive Decay:
Radioactive decay is the process in which a radioactive isotope emits radiation and transforms into another element. This new atom may be stable, or it may also be radioactive and undergo further decay.
Uranium-238 decays into Pa-234 as followed:
Step 1:
$\ce{^{238}_{92}U -> ^{234}_{90}Th + \text{energy}}$
Step 2:
$\ce{^{234}_{90}Th -> ^{231}_{91}Pa + \text{energy}}$
(Correction: In the book, it says that Th-234 decays into Pa-231, but this is incorrect. Th-234 actually decays into Pa-234.)
Bismuth-210 decays into thallium-206 as followed:
$\ce{^{210}_{83}Bi -> ^{206}_{81}Tl + \text{energy}}$
Q3. What are the applications of radioactive isotopes?
- Technetium-99m is used in medical imaging for organs like the brain, lungs, etc. Patients are injected with a small amount of this radioactive isotope, and then a special camera is used to monitor the movement of the radioactive fluid.
- Radioactive isotopes are used to diagnose and treat many diseases like cancer and thyroid disorders.
- They are also used to test the strength of metals and concrete mixtures.
- The radioactive isotope C-14 is used to determine the age of carbon-containing materials. The age of a sample (bone, wood, etc.) is measured by determining the proportion of C-14. The older the sample, the less C-14 is detected.
- Radioactive isotopes are also used to ionize atoms. For example, radium-226 can ionize atoms through its radiation. This process converts the atom into a cation (positive ion).
Q4. Write a note on ionization of atoms by a radioactive source.
Radiation emitted from a radioactive isotope can collide with an atom and remove tightly bound electron from its orbit. This is called ionization of atoms by a radioactive source.
For example, radiation from radioactive radium-226 has enough energy that its ionizing radiation can collide with a sodium atom and forces the electron away from it. This process converts that sodium atom into a cation.
$\ce{Na ->[\text{Energy}] Na+ + e-}$