9.2.2 Discovery of Electrons
This is the second lecture from Chapter 2: ‘Atomic Structure’ of the new book for Class 9 Chemistry (Punjab Board – PCTB). It covers the discovery of electrons through discharge tube experiments. The lecture includes a multiple-choice quiz, short-answer questions, and detailed long-answer notes.
MCQs Based Quiz
Short Questions
Q1. What is a discharge tube, and what are its main components?
A discharge tube is a hard glass tube that has three main components:
- A vacuum pump to decrease the pressure of gas inside the tube
- A very high voltage power source
- Two electrodes at both ends of the tube.
Q2. How can you produce cathode rays in a discharge tube?
- The gas pressure is reduced using a vacuum pump.
- A high voltage power source is connected to the electrodes.
- A glow appears behind the positive electrode (anode), indicating the generation of cathode rays.
Q3. Define cathode rays.
Cathode rays are negatively charged particles (electrons) that originate from the cathode when a very high voltage is applied across a discharge tube at low pressure.
Q4. What were two important observations J.J. Thomson made in the discharge tube experiment?
- The cathode rays were deflected toward the positively charged plate, indicating that they carry a negative charge.
- Their path was also deflected by a magnetic field
Q5. Write two properties of cathode rays.
- They are deflected towards the positively charged plate.
- They are also deflected by a magnetic field.
Descriptive Question
Q1. Write a comprehensive note on the discovery of electrons.
The discovery of electrons is primarily attributed to the discharge tube experiments.
Construction of a Discharge Tube:
A discharge tube is a hard glass tube that has three main components:
- A vacuum pump to decrease the pressure of gas inside the tube
- A very high voltage power source
- Two electrodes at both ends of the tube.
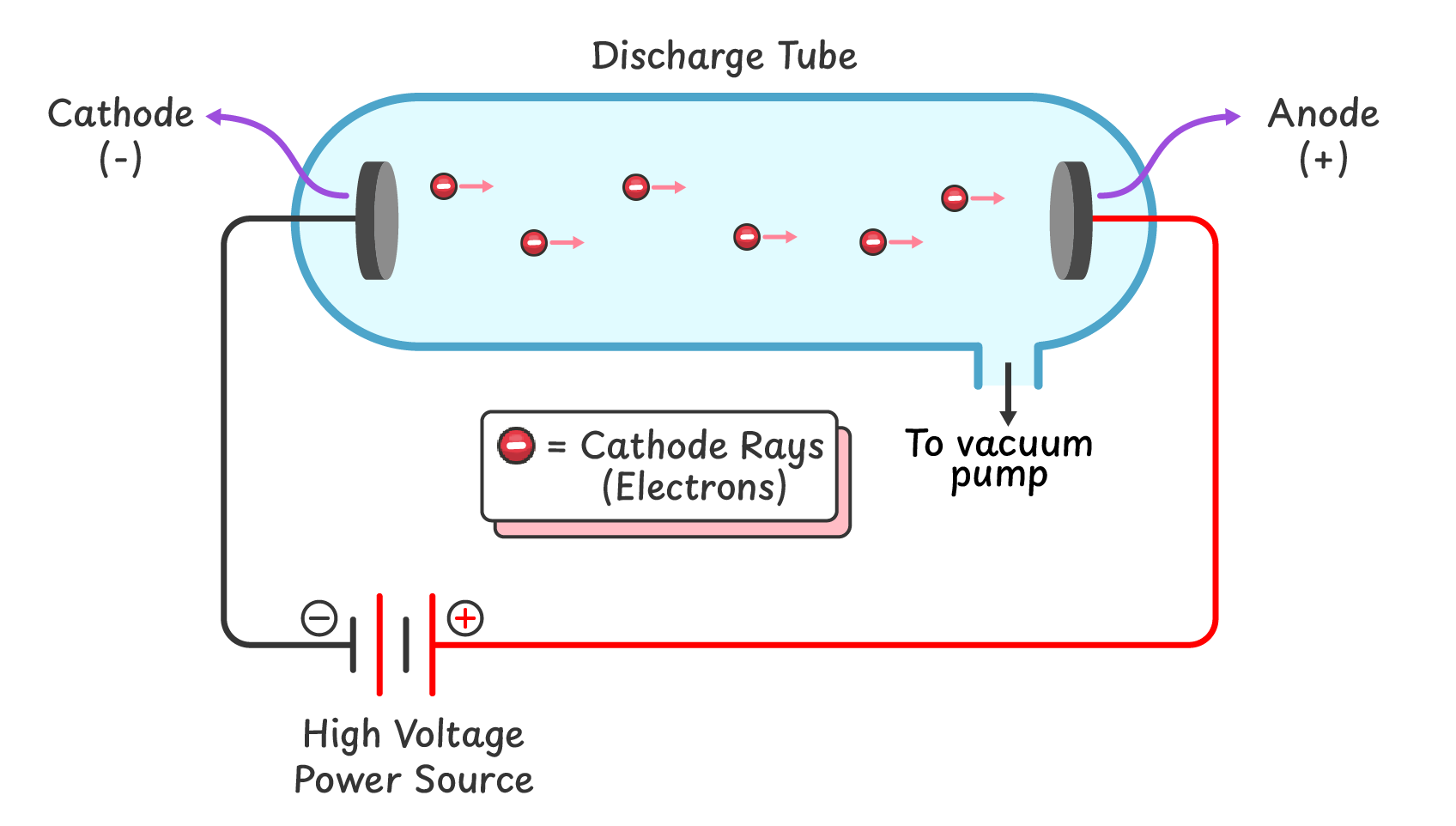
Production of Cathode Rays:
When a very high voltage is applied across the electrodes at very low gas pressure, a glow appears on the glass behind the positive electrode. This glow is caused by rays emitted from the cathode, known as cathode rays.
Observations of J. J. Thomson:
In 1897, a British physicist Joseph John Thomson conducted several experiments and made the following observations:
- When cathode rays were passed through oppositely charged electric plates, they bent towards the positive plate. This showed that the rays carry negative charge.
- A magnetic field also deflected the rays, further confirming their charged nature.
- Thomson measured the mass-to-charge ratio of these rays and concluded that they consisted of negatively charged particles.
- He identified these negatively charged particles as a new type of sub-atomic particle, later named electrons.
This discovery marked the first identification of a particle smaller than the atom and laid the foundation for modern atomic theory.